South Korea 5G IoT Market Outlook to 2029
By Applications, By Industry Verticals, By Network Type, By Deployment Mode, and By Region.
- Product Code: TDR0104
- Region: Asia
- Published on: December 2024
- Total Pages: 110
Report Summary
The report titled “South Korea 5G IoT Market Outlook to 2029 – By Applications, By Industry Verticals, By Network Type, By Deployment Mode, and By Region.” provides a comprehensive analysis of the 5G IoT market in South Korea. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the 5G IoT Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by market, applications, region, cause and effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
South Korea 5G IoT Market Overview and Size
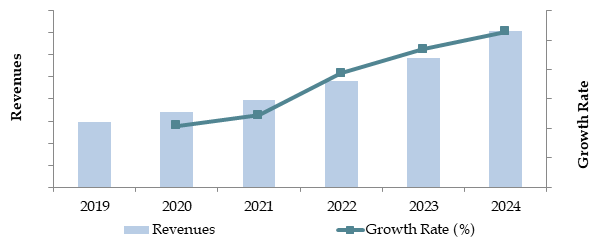
The South Korea 5G IoT market reached a valuation of KRW 9.5 Trillion in 2023, driven by the rapid adoption of 5G infrastructure, government initiatives to promote IoT technologies, and increasing demand for smart city solutions. The market is characterized by major players such as SK Telecom, KT Corporation, LG U+, and Samsung Electronics, known for their cutting-edge technologies, extensive service portfolios, and strong market presence.
In 2023, KT Corporation launched a new 5G IoT solution targeting the industrial and healthcare sectors, enabling enhanced connectivity and operational efficiency. Seoul and Busan are key markets due to their high population density and advanced technological infrastructure.
Market Size for South Korea 5G IoT Industry on the Basis of Revenue in KRW Trillion, 2018-2024
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of South Korea 5G IoT Market:
Technological Advancements: The rollout of advanced 5G networks has significantly improved data speeds and reduced latency, creating a favorable environment for IoT applications. In 2023, over 80% of IoT devices in South Korea utilized 5G connectivity, making it a global leader in IoT technology adoption.
Government Support: The South Korean government has invested heavily in 5G infrastructure and IoT development as part of its "Digital New Deal" initiative. This has led to the establishment of smart cities and the integration of IoT in public services such as transportation and healthcare.
Industrial IoT Adoption: The manufacturing sector in South Korea is rapidly adopting IoT solutions for automation and predictive maintenance. In 2023, industrial IoT applications accounted for 35% of the total 5G IoT market revenue, driven by increased demand for operational efficiency and real-time monitoring.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of South Korea 5G IoT Market
Infrastructure Costs: High costs associated with the deployment and maintenance of 5G infrastructure pose a significant challenge. According to industry data, approximately 35% of telecom operators in South Korea cite the financial burden of 5G network expansion as a major hurdle, slowing the rollout of IoT solutions in less densely populated areas.
Security Concerns: As IoT devices become more interconnected, security vulnerabilities remain a critical challenge. A 2023 report indicated that 40% of South Korean businesses using IoT solutions expressed concerns about potential cybersecurity risks, including data breaches and device hacking, which deter broader adoption.
Limited Standardization: The lack of standardized protocols for 5G IoT integration across industries creates fragmentation. In 2023, over 25% of IoT solution providers in South Korea faced compatibility issues, impacting the scalability and interoperability of IoT systems.
Adoption Barriers in SMEs: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often struggle with the cost and complexity of integrating IoT technologies. In South Korea, only 18% of SMEs have adopted IoT solutions as of 2023, citing resource constraints and limited expertise as primary barriers.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives Governing the Market
5G Infrastructure Development Support: The South Korean government has launched extensive programs to subsidize the development of 5G networks, particularly in rural and underserved regions. In 2023, government grants supported 15% of new 5G infrastructure projects, helping to reduce deployment costs and accelerate coverage expansion.
Data Privacy Regulations: To protect consumer data, the Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) enforces stringent regulations on data handling by IoT service providers. In 2023, 92% of companies in the IoT sector reported compliance with PIPA, ensuring greater consumer trust in IoT applications.
Smart City Initiatives: The government has been actively promoting smart city projects as part of its "Digital New Deal" initiative. These projects include the integration of IoT devices for traffic management, energy efficiency, and public safety. In 2023, smart city-related IoT solutions contributed 22% to the total 5G IoT market revenue.
South Korea 5G IoT Market Segmentation
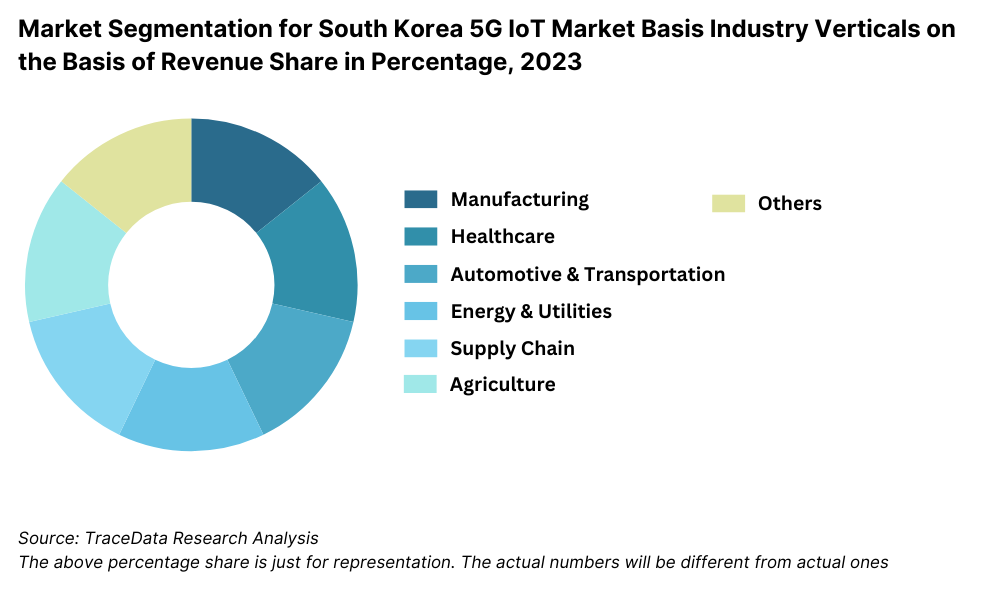
By Industry Verticals: The industrial sector dominates the 5G IoT market in South Korea due to its early adoption of IoT technologies for automation, predictive maintenance, and quality control. The healthcare sector holds a significant share as hospitals and clinics increasingly adopt IoT-enabled devices for real-time monitoring and patient care. The transportation sector also plays a vital role, leveraging IoT for smart traffic systems and autonomous vehicles.
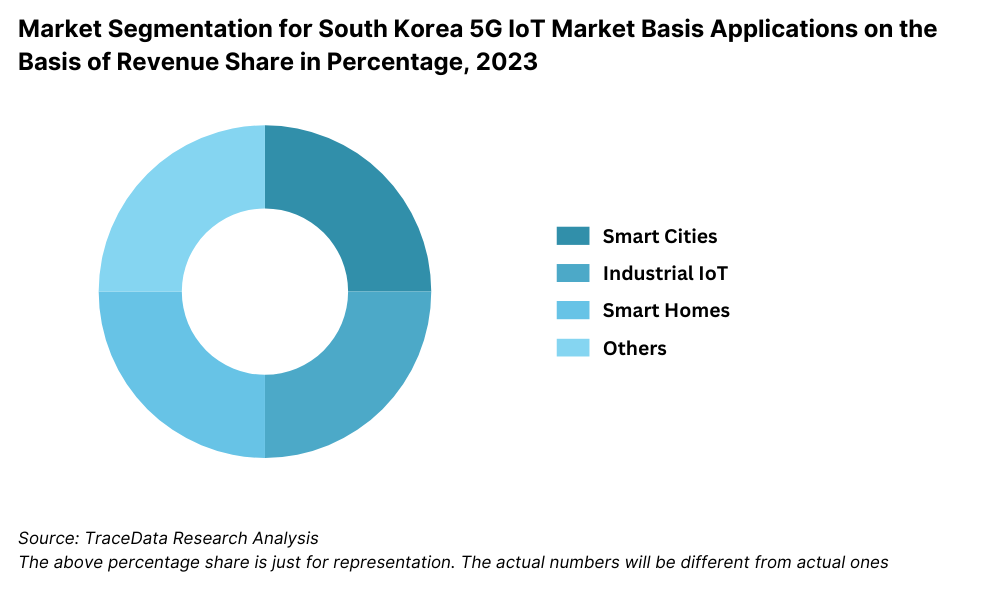
By Applications: Smart city solutions lead the market, driven by government-backed initiatives to enhance urban infrastructure through IoT technologies. Industrial IoT follows closely, with applications in manufacturing, logistics, and energy management gaining traction. Consumer IoT, including smart home devices and wearables, represents a growing segment, particularly among tech-savvy urban consumers.
By Network Type: Standalone 5G networks are becoming increasingly prevalent as they provide the low latency and high-speed connectivity necessary for advanced IoT applications. However, non-standalone 5G networks still hold a significant share, catering to regions where infrastructure upgrades are ongoing.
Competitive Landscape in South Korea 5G IoT Market
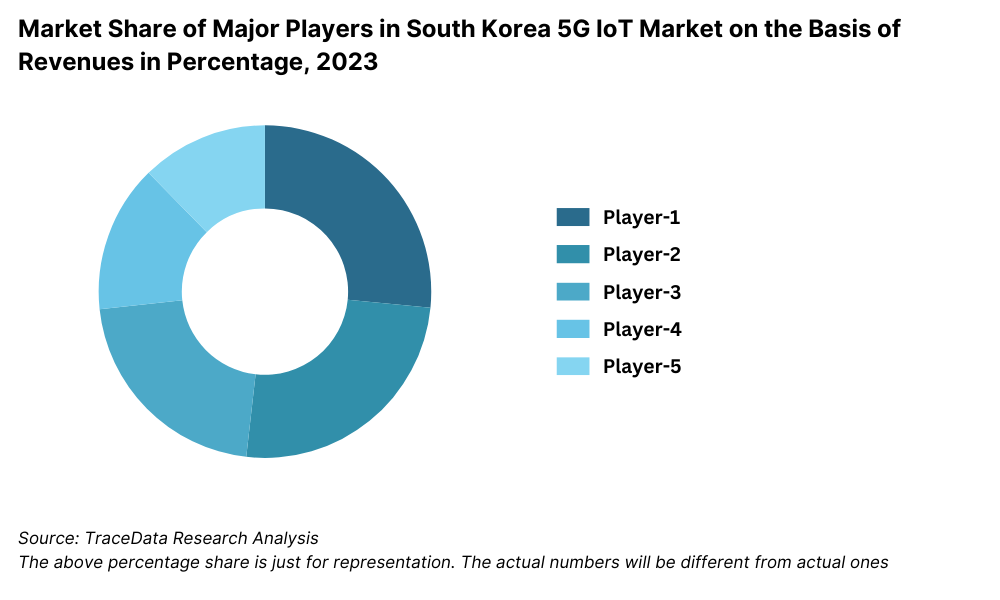
The South Korea 5G IoT market is moderately concentrated, with several established players and a growing number of new entrants driving innovation and competition. Key companies such as SK Telecom, KT Corporation, LG U+, and Samsung Electronics lead the market, supported by government-backed initiatives and cutting-edge R&D efforts.
Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|
SK Telecom | 1984 | Seoul, South Korea |
KT Corporation | 1981 | Seongnam, South Korea |
LG Uplus | 1996 | Seoul, South Korea |
Samsung Electronics | 1969 | Suwon, South Korea |
LG Electronics | 1958 | Seoul, South Korea |
Hyundai Motor Company | 1967 | Seoul, South Korea |
Naver Corporation | 1999 | Seongnam, South Korea |
Kakao Corporation | 2010 | Jeju, South Korea |
Hanwha Systems | 1977 | Seoul, South Korea |
POSCO ICT | 1989 | Pohang, South Korea |
Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors
SK Telecom: As the largest telecom operator in South Korea, SK Telecom reported a 30% increase in its IoT-related revenue in 2023. The company’s investments in smart city projects and industrial IoT solutions, such as real-time monitoring systems for factories, have reinforced its leadership in the market.
KT Corporation: KT Corporation launched a new 5G-enabled IoT platform in 2023, targeting healthcare and industrial automation. The platform’s advanced analytics and AI integration helped KT achieve a 25% growth in its IoT business revenue.
LG U+: Specializing in consumer IoT and smart home technologies, LG U+ saw a 20% growth in revenue from IoT devices in 2023. Its recent collaboration with smart appliance manufacturers has strengthened its foothold in the residential sector.
Samsung Electronics: Leveraging its expertise in electronics and semiconductors, Samsung Electronics introduced several 5G IoT-enabled devices in 2023, including smart wearables and industrial sensors. The company recorded a 15% increase in IoT product sales, driven by strong demand in domestic and international markets.
What Lies Ahead for South Korea 5G IoT Market?
The South Korea 5G IoT market is projected to grow robustly by 2029, exhibiting a strong CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is expected to be driven by rapid technological advancements, increasing government investments, and the rising adoption of IoT across various industry verticals.
Expansion of Smart Cities: South Korea’s continued investment in smart city initiatives is expected to drive the adoption of 5G IoT solutions for traffic management, public safety, and energy efficiency. Cities like Seoul and Busan are anticipated to lead these developments, further solidifying South Korea as a global leader in smart city innovation.
Increased Adoption of Industrial IoT: The manufacturing and logistics sectors are projected to remain at the forefront of 5G IoT adoption, with a focus on automation, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization. The introduction of edge computing technologies is expected to enhance operational efficiencies, further driving market growth.
Rise of Healthcare IoT: The healthcare sector is expected to experience significant growth, with the integration of IoT devices for remote patient monitoring, smart medical devices, and real-time health analytics. This trend is supported by an aging population and increasing demand for advanced medical solutions.
Advances in Consumer IoT: The demand for smart home devices, wearables, and connected appliances is expected to grow steadily, driven by tech-savvy consumers and the convenience offered by IoT-enabled technologies. Companies are likely to focus on improving interoperability and user experience to attract a wider audience.
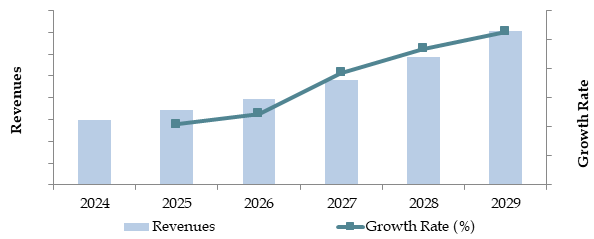
Future Outlook and Projections for South Korea 5G IoT Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029
South Korea 5G IoT Market Segmentation
- By Industry Verticals:
- Manufacturing
- Healthcare
- Transportation and Logistics
- Energy and Utilities
- Smart Cities
- Consumer Electronics
- Retail
- Others
- By Component:
- Hardware
- Platform
- Connectivity
- Services
- By Applications:
- Smart Cities Solutions
- Industrial IoT
- Connected Healthcare
- Smart Homes
- Wearables
- Autonomous Vehicles
- By Network Type:
- Standalone 5G Networks
- Non-Standalone 5G Networks
- By Deployment Mode:
- Cloud-Based
- Edge Computing
- By Region:
- Seoul
- Busan
- Incheon
- Daegu
- Daejeon
- Gwangju
- Other Regions
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- SK Telecom
- KT Corporation
- LG Uplus
- Samsung Electronics
- LG Electronics
- Hyundai Motor Company
- Naver Corporation
- Kakao Corporation
- Hanwha Systems
- POSCO ICT
Key Target Audience:
- Telecom Operators
- IoT Device Manufacturers
- Government Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Science and ICT)
- Technology Solution Providers
- Research and Development Institutions
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018-2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in South Korea 5G IoT Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process – Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges
4.2. Revenue Streams for South Korea 5G IoT Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for South Korea 5G IoT Market
4.4. Buying Decision-Making Process
4.5. Supply Decision-Making Process
5. Market Structure
5.1. South Korea IoT Device Adoption Trends, 2018-2024
5.2. IoT Network Penetration (4G vs. 5G) in South Korea, 2018-2024
5.3. Telecom Sector Spend on IoT Infrastructure, 2024
6. Market Attractiveness for South Korea 5G IoT Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for South Korea 5G IoT Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for South Korea 5G IoT Market Basis
9.1. By Industry Verticals (Manufacturing, Healthcare, Automotive & Transportation, Energy and Utilities, Supply Chain & Logistics, Agriculture, Government & Public Safety and others), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Component (Hardware, Platform, Connectivity and Services), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Applications (Smart Cities, Industrial IoT, Smart Homes and others), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Network Type (Standalone, Non-Standalone), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Deployment Mode (Cloud, Edge Computing), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (Seoul, Busan, Incheon, and others), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for South Korea 5G IoT Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making Process
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments in South Korea 5G IoT Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for South Korea 5G IoT Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for South Korea 5G IoT Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges in South Korea 5G IoT Market
11.5. Government Regulations for South Korea 5G IoT Market
12. Snapshot on IoT Devices Market in South Korea
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for IoT Devices, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading IoT Device Providers Basis Operational and Financial Parameters
13. Opportunity Matrix for South Korea 5G IoT Market – Presented with the Help of Radar Chart
14. PEAK Matrix Analysis for South Korea 5G IoT Market
15. Competitor Analysis for South Korea 5G IoT Market
15.1. Market Share of Major Players in South Korea 5G IoT Market, 2023
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors in South Korea 5G IoT Market Basis Operational and Financial Variables
15.3. Strengths and Weaknesses
15.4. Operating Model Analysis Framework
15.5. Gartner Magic Quadrant
15.6. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. Future Market Size for South Korea 5G IoT Market Basis
16.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17. Market Breakdown for South Korea 5G IoT Market Basis
17.1. By Industry Verticals (Manufacturing, Healthcare, Automotive & Transportation, Energy and Utilities, Supply Chain & Logistics, Agriculture, Government & Public Safety and others), 2025-2029
17.2. By Component (Hardware, Platform, Connectivity and Services), 2025-2029
17.2. By Applications (Smart Cities, Industrial IoT, Smart Homes and others), 2025-2029
17.3. By Network Type (Standalone, Non-Standalone), 2025-2029
17.4. By Deployment Mode (Cloud, Edge Computing), 2025-2029
17.5. By Region (Seoul, Busan, Incheon, and others), 2025-2029
18. Recommendation
18.1. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand and supply side entities for South Korea 5G IoT Market. Based on this ecosystem, shortlist leading 5-6 players in the country based on their financial performance, technological capabilities, and market share.
Sourcing is conducted through industry reports, articles, and multiple secondary and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market and collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Conduct exhaustive desk research by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to aggregate industry-level insights, delving into aspects such as market revenue, number of market players, adoption rates, and pricing trends.
Supplement findings with detailed examinations of company-level data, leveraging sources such as press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and expert articles to build a comprehensive understanding of the market and its key players.
Step 3: Primary Research
Conduct in-depth interviews with C-level executives, key stakeholders, and end-users in the South Korea 5G IoT market. This validates market hypotheses, authenticates statistical data, and provides insights into operational strategies and challenges.
A bottom-to-top approach is undertaken to evaluate the contribution of each player, thereby aggregating their market shares to form an overall market estimate.
Disguised interviews are executed by posing as potential customers to validate data shared by executives, corroborating this against secondary sources. These interactions help in analyzing revenue streams, the value chain, and pricing models.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A combination of bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analysis, along with market size modeling, ensures a thorough sanity check process for the final market estimates and projections.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the South Korea 5G IoT Market?
The South Korea 5G IoT market is poised for substantial growth, projected to reach a valuation of KRW 15 Trillion by 2029. This growth is driven by rapid technological advancements, government-backed initiatives, and increasing IoT adoption across industry verticals.
2. Who are the Key Players in the South Korea 5G IoT Market?
The South Korea 5G IoT market features several key players, including SK Telecom, KT Corporation, LG U+, and Samsung Electronics. These companies dominate due to their extensive technological capabilities, robust network infrastructure, and strong market presence.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the South Korea 5G IoT Market?
The primary growth drivers include advancements in 5G technology, government investments in smart city initiatives, and increased IoT adoption in industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. The growing demand for smart home devices and wearables also contributes to market expansion.
4. What are the Challenges in the South Korea 5G IoT Market?
The South Korea 5G IoT market faces challenges such as high infrastructure costs, cybersecurity concerns, and the lack of standardized protocols for IoT device integration. Additionally, adoption barriers among SMEs due to cost and complexity further hinder market growth