Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Segments, By Product Offerings, By Customer Base, By Geographic Region, and By Growth Drivers
- Product Code: TDR0092
- Region: Asia
- Published on: December 2024
- Total Pages: 110
Report Summary
The report titled “Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Segments, By Product Offerings, By Customer Base, By Geographic Region, and By Growth Drivers” provides a comprehensive analysis of the Islamic banking market in Malaysia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, the overall market size in terms of assets and revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and a comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Islamic banking sector. The report concludes with future market projections based on assets, customer base, product segments, regions, cause-and-effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting major opportunities and cautions.
Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Overview and Size
The Malaysia Islamic banking market reached an asset valuation of MYR 1.5 trillion in 2023, driven by increasing demand for Shariah-compliant financial services, a growing Muslim population, and favorable government policies promoting Islamic finance. The market is characterized by major players such as Maybank Islamic, CIMB Islamic, Bank Islam Malaysia, RHB Islamic Bank, and AmBank Islamic. These institutions are recognized for their extensive product offerings, innovative digital banking solutions, and adherence to Shariah principles.
In 2023, Bank Islam launched a new digital platform to enhance customer experience and provide a wider range of Shariah-compliant banking services. This initiative aligns with Malaysia’s digital transformation goals and caters to the rising demand for convenient, technology-driven banking solutions. Key markets such as Kuala Lumpur and Selangor are at the forefront due to their high population density and advanced financial infrastructure.
Market Size of Malaysia Islamic Banking Industry by Loan Outstanding/Credit Disbursed in USD Billion, 2018-2024
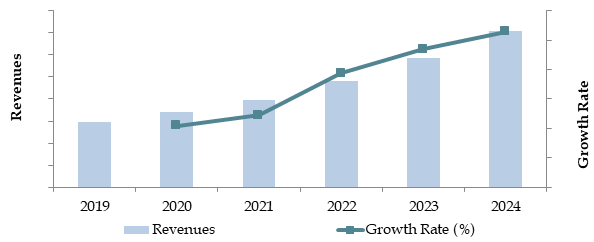
Source: TraceData Research Analysis
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Malaysia Islamic Banking Market?
Regulatory Support and Government Initiatives: Malaysia's government has actively supported the growth of Islamic banking through policies and frameworks such as the Financial Sector Blueprint (2022–2026), which aims to enhance the sector's contribution to the national economy. As of 2023, Islamic finance constitutes approximately 38% of the total financial assets in Malaysia, highlighting the effectiveness of these initiatives.
Increased Awareness of Shariah Compliance: The growing awareness and preference for Shariah-compliant financial products among Malaysia's predominantly Muslim population have fueled the expansion of the Islamic banking sector. Over 65% of new financial accounts opened in 2023 were Islamic, reflecting the increasing inclination towards ethical and interest-free banking.
Digital Transformation: The rise of fintech and digital banking solutions has revolutionized the Islamic banking market, enhancing accessibility and operational efficiency. In 2023, over 50% of Islamic banking transactions in Malaysia were conducted through digital platforms, signifying a shift towards tech-driven customer engagement. Banks have invested heavily in AI-powered chatbots, mobile apps, and blockchain to ensure compliance and customer satisfaction.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of Malaysia Islamic Banking Market?
Limited Awareness and Education: A significant challenge is the limited understanding of Islamic banking principles among the public. According to a 2023 industry survey, approximately 58% of consumers are unaware of the benefits of Islamic banking products, with many perceiving them as being exclusively for Muslims. This lack of awareness has deterred adoption among non-Muslim populations, restricting market expansion.
Regulatory Variability: The Islamic banking sector encounters difficulties in achieving uniform Shariah compliance across institutions. In 2023, around 15% of products offered by Islamic banks faced criticism for inconsistent adherence to Shariah principles. This issue has created trust deficits and confusion among customers, impacting market penetration.
Digital Transformation Challenges: While digital banking is growing rapidly, Islamic banks lag in adopting advanced technologies. Approximately 40% of customers in 2023 reported dissatisfaction with the digital banking services provided by Islamic banks compared to their conventional counterparts, indicating a gap in service delivery and technological innovation.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives Which Have Governed the Market?
Shariah Governance Framework: The Central Bank of Malaysia introduced a robust Shariah governance framework to ensure all Islamic banking products comply with Islamic principles. In 2022, more than 90% of Islamic banks were rated compliant under the framework, boosting consumer confidence and promoting market growth.
Incentives for Halal Financing: The Malaysian government offers tax incentives for financial institutions that provide halal financing solutions. In 2023, these incentives led to a 12% increase in Islamic home financing, reflecting their effectiveness in driving sector growth.
Digital Banking Licenses: Bank Negara Malaysia issued digital banking licenses in 2022, encouraging Islamic banks to enhance their digital offerings. As of 2023, four Islamic banks had announced plans to launch fully digital banking platforms by 2025, aiming to capture the growing tech-savvy customer base.
Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Segmentation
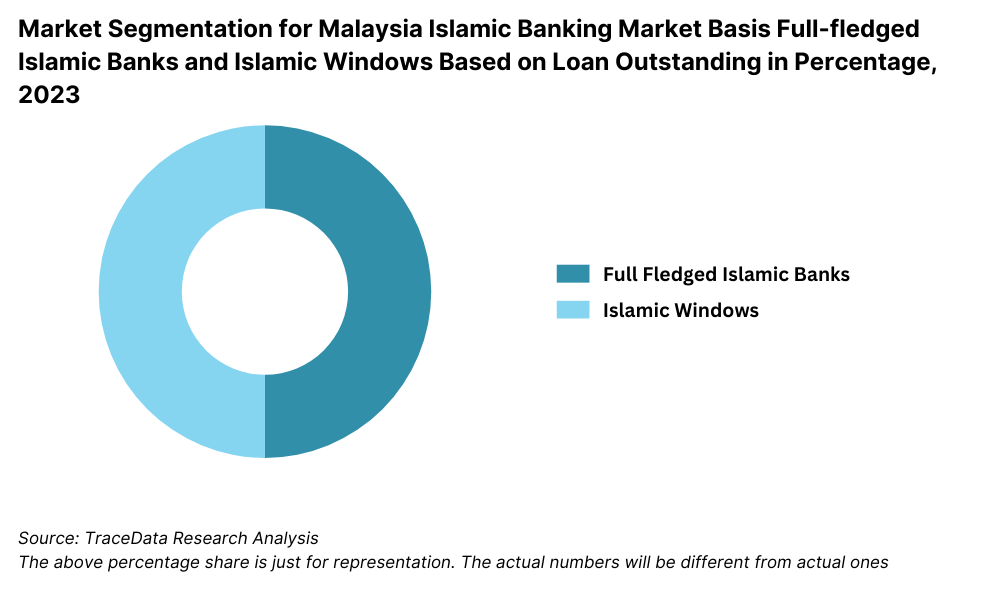
By Market Structure: The Islamic banking market in Malaysia is dominated by full-fledged Islamic banks, which account for the majority share due to their extensive focus on Shariah-compliant products and services. These banks cater specifically to customers seeking financial solutions that align with Islamic principles. Conventional banks with Islamic windows hold a significant share, offering hybrid models that appeal to a wider customer base, including those transitioning from conventional to Islamic banking. This dual approach allows these banks to capture diverse customer segments while maintaining compliance with Shariah guidelines.
By Product Offerings: Murabaha (cost-plus financing) remains the most popular product in the Islamic banking market, owing to its simplicity and alignment with Shariah principles. Customers value its transparency and fixed repayment structure, making it a preferred choice for financing needs. Sukuk (Islamic bonds) is a growing segment, driven by Malaysia's position as a global leader in sukuk issuance. The demand for takaful (Islamic insurance) has also risen significantly due to increased awareness of risk-sharing mechanisms, particularly for life and health coverage.

By Customer Base: The retail segment dominates the Islamic banking customer base, comprising individuals who seek personal financing, home financing, and deposit products. This segment benefits from targeted campaigns promoting Islamic banking's ethical approach. The corporate and SME segment follows, driven by businesses requiring Shariah-compliant financing for working capital and asset acquisition. Government institutions also represent a growing customer base, leveraging Islamic finance for infrastructure and public projects.
Competitive Landscape in Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
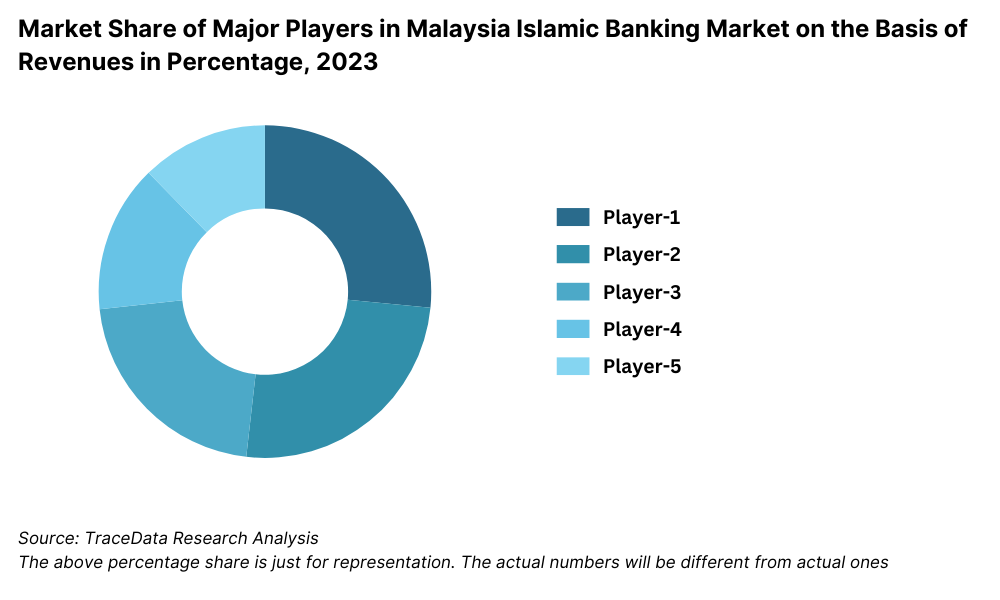
The Malaysia Islamic banking market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of dedicated Islamic banks and conventional banks offering Islamic windows. Major players such as Maybank Islamic, CIMB Islamic, Bank Islam Malaysia Berhad, RHB Islamic, and Public Islamic Bank dominate the space. Meanwhile, smaller Islamic financial institutions and fintech startups are gradually increasing competition by offering niche services and innovative digital products.
Bank Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|
Bank Islam Malaysia Berhad | 1983 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
Maybank Islamic Berhad | 2008 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
CIMB Islamic Bank Berhad | 2003 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
RHB Islamic Bank Berhad | 2005 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
AmBank Islamic Berhad | 2006 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
Affin Islamic Bank Berhad | 2006 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
Bank Muamalat Malaysia Berhad | 1999 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
Hong Leong Islamic Bank Berhad | 2005 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
Public Islamic Bank Berhad | 2008 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
Alliance Islamic Bank Berhad | 2007 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Maybank Islamic: As the largest Islamic bank in Malaysia by assets, Maybank Islamic accounted for over 30% of the market share in 2023. The bank introduced a new Shariah-compliant digital savings account in 2023, attracting over 100,000 new customers within the first six months.
CIMB Islamic: Known for its focus on sustainability, CIMB Islamic launched several green financing products in 2023, including renewable energy project financing. The bank reported a 15% year-on-year growth in financing disbursements for green initiatives, aligning with Malaysia's ESG goals.
Bank Islam Malaysia Berhad (BIMB): As a pioneer in Islamic banking, BIMB recorded a 20% growth in SME financing in 2023. The bank’s recent launch of an Islamic digital wallet has enhanced its appeal among younger, tech-savvy customers.
RHB Islamic: RHB Islamic is leveraging technology to expand its presence, with a 12% increase in active users of its mobile banking app in 2023. The bank's focus on personalized financial planning tools for customers has been a key differentiator.
Public Islamic Bank: Public Islamic Bank reported a 10% increase in Islamic personal financing in 2023. Its strength lies in its extensive branch network, which ensures accessibility for customers in both urban and rural areas.
What Lies Ahead for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market?
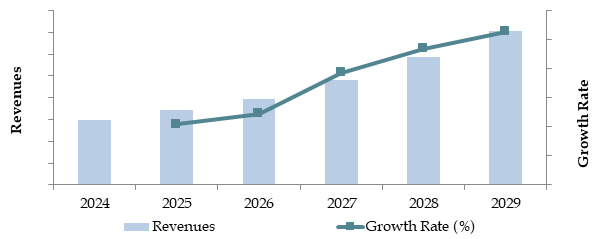
The Malaysia Islamic banking market is projected to grow steadily by 2029, exhibiting a robust CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is expected to be driven by increasing consumer demand for Shariah-compliant financial products, government support, and advancements in digital banking technologies.
Expansion of Digital Islamic Banking Services: The ongoing digital transformation within the Islamic banking sector is anticipated to accelerate. With the issuance of digital banking licenses by Bank Negara Malaysia, several Islamic banks are expected to launch fully digital platforms, providing customers with more accessible and innovative Shariah-compliant banking solutions.
Growth in ESG-Linked Financing: Islamic banking’s alignment with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles positions it well to support Malaysia's sustainability goals. Products like Islamic green financing and sukuk linked to ESG initiatives are anticipated to grow significantly, fueled by both consumer demand and regulatory encouragement.
Increased Adoption of Takaful (Islamic Insurance): The takaful sector is expected to expand further as awareness of Islamic insurance grows. New digital takaful platforms offering simplified enrollment and claims processes are likely to attract a younger, tech-savvy demographic.
Development of SME Financing: Islamic banks are projected to play a pivotal role in supporting small and medium enterprises (SMEs) by offering tailored Shariah-compliant financing products. This segment is expected to grow as the Malaysian government prioritizes SME development as a key driver of economic growth.
Future Outlook and Projections for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029
Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Segmentation
By Market Structure:
Full-fledged Islamic Banks
Islamic Windows of Conventional Banks
Digital Islamic Banks
Cooperative Islamic Banks
By Product Offerings:
Murabaha (Cost-Plus Financing)
Ijarah (Leasing)
Sukuk (Islamic Bonds)
Takaful (Islamic Insurance)
Musharaka (Partnership Financing)
Wadiah (Safe Custody Accounts)
Islamic Personal Loans
Islamic Home Financing
By Customer Base:
Retail Banking
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Corporate Banking
Government and Public Institutions
By Retail
Murabaha
Ijara
Diminishing Musharaka
Qard Hasan
Tawarruq
By SME Loans
Murabaha
Istisna
Ijara
Mudarabah
Musharaka
Qard Hasan
By Corporate Banking Loans
Murabaha
Ijara
Istisna
Mudarabah
Musharaka
Sukuk
Tawarruq
By Government and Public Institution Loans
Ijara
Istisna
Musharaka
Sukuk
Qard Hasan
Murabaha
By Region:
Central (e.g., Klang Valley)
Northern (e.g., Penang)
Southern (e.g., Johor)
Eastern (e.g., Kelantan, Terengganu)
East Malaysia (e.g., Sabah, Sarawak)
By Target Market Segment:
Muslim Population
Non-Muslim Population Interested in Ethical Banking
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Bank Islam Malaysia Berhad
Maybank Islamic Berhad
CIMB Islamic Bank Berhad
RHB Islamic Bank Berhad
AmBank Islamic Berhad
Affin Islamic Bank Berhad
Bank Muamalat Malaysia Berhad
Hong Leong Islamic Bank Berhad
Public Islamic Bank Berhad
Alliance Islamic Bank Berhad
Key Target Audience:
Full-fledged Islamic Banks
Conventional Banks with Islamic Windows
Fintech Companies Specializing in Islamic Finance
Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Bank Negara Malaysia)
Research and Development Institutions in Islamic Finance
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2018-2023
Base Year: 2024
Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process - Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
4.4. Customer Decision-Making Process
5. Market Structure
5.1. Market Share of Full-Fledged Islamic Banks vs. Islamic Windows, 2018-2024
5.2. Asset Growth of Malaysia Islamic Banking Sector, 2018-2024
5.3. Penetration of Islamic Banking Products in Malaysia, 2024
5.4. Number of Islamic Banks by Region in Malaysia
6. Market Attractiveness for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Basis
8.1. Loan Outstanding, 2018-2024
8.2. Credit Disbursed, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Full-Fledged Banks, Islamic Windows), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Product Offering (Murabaha, Ijarah, Sukuk, Takaful), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Customer Base (Retail, SMEs, Corporate, Government), 2023-2024P
9.3.1. By Type of Retail Loans, 2023-2024P
9.3.2. By Type of SME Loans, 2023-2024P
9.3.3. By Type of Corporate Loans, 2023-2024P
9.4. By Region (Central, Northern, Southern, Eastern, East Malaysia), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
11.1. Trends and Developments for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
12. Snapshot on Digital Islamic Banking Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Digital Islamic Banking Market, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross-Comparison of Leading Islamic Banks in Malaysia Basis Operational and Financial Indicators
13. Opportunity Matrix for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market - Presented with the Help of Radar Chart
14. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
15. Competitor Analysis for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market
15.1. Market Share of Key Players in Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Basis Loan Outstanding/Credit Disbursed, 2024
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Basis Operational and Financial Variables
15.3. Strength and Weakness
15.4. Operating Model Analysis Framework
15.5. Gartner Magic Quadrant
15.6. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. Future Market Size for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Basis
16.1. Loan Outstanding, 2025-2029
16.2. Credit Disbursed, 2025-2029
16. Market Breakdown for Malaysia Islamic Banking Market Basis
16.1. By Market Structure (Full-Fledged Banks, Islamic Windows), 2025-2029
16.2. By Product Offering (Murabaha, Ijarah, Sukuk, Takaful), 2025-2029
16.3. By Customer Base (Retail, SMEs, Corporate, Government), 2025-2029
16.1.1. By Type of Retail Loans, 2025-2029
16.1.2. By Type of SME Loans, 2025-2029
16.1.3. By Type of Corporate Loans, 2025-2029
16.1.4. By Region (Central, Northern, Southern, Eastern, East Malaysia), 2025-2029
17. Recommendations
18.1. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Malaysia Islamic Banking Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 banks in the country based on their financial information, total assets, product offerings, and market share.
Sourcing is made through industry reports, regulatory publications, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market and collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights.
We delve into aspects such as total banking assets, customer segmentation, product categories, and other variables. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, Shariah governance frameworks, and financial statements. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Malaysia Islamic Banking Market companies and regulatory bodies. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives.
Bottom-to-top approach is undertaken to evaluate total assets and revenue contributions of each player, thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of revenue streams, value chains, Shariah compliance processes, and pricing.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess the sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Malaysia Islamic Banking Market?
The Malaysia Islamic banking market is poised for substantial growth, projected to reach a valuation of MYR 1.5 trillion by 2029. This growth is driven by increasing consumer demand for Shariah-compliant financial products, government incentives, and advancements in digital banking technologies.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Malaysia Islamic Banking Market?
The Malaysia Islamic Banking Market features several key players, including Maybank Islamic, CIMB Islamic, and Bank Islam Malaysia Berhad. These institutions dominate the market due to their extensive distribution networks, comprehensive product offerings, and significant total assets. Other notable players include RHB Islamic and Public Islamic Bank.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Malaysia Islamic Banking Market?
The primary growth drivers include government support through regulatory frameworks, increasing awareness of Shariah-compliant products, and the integration of Islamic banking with ESG goals. Digital transformation within the sector and the growing SME segment further contribute to market expansion.
4. What are the Challenges in the Malaysia Islamic Banking Market?
The Malaysia Islamic Banking Market faces several challenges, including limited public awareness, regulatory variability in Shariah compliance, and strong competition from conventional banks. Additionally, digital transformation barriers and the slow pace of technology adoption hinder growth potential.