Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Regions, By Target Demographics, By Popular Activities, By Key Destinations, and By Modes of Transport
- Product Code: TDR0089
- Region: Asia
- Published on: December 2024
- Total Pages: 110

Want to Assess the Impact of US-Imposed Trade Tariff on
Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
Report Summary
The report titled “Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By Regions, By Target Demographics, By Popular Activities, By Key Destinations, and By Modes of Transport” provides a comprehensive analysis of the eco-tourism market in Indonesia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue and tourist volume, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and profiling of major players in the Eco-Tourism Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, tourist volume, market segmentation, region, cause and effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Overview and Size
With evolving awareness about the environment during global tourism and the diversities of Indonesia promoted through various governmental initiatives towards eco-friendly travels, by 2023, eco-tourism in the Indonesian market attained a value at approximately IDR 45 trillion, further fueled by growing, global awareness about sustainable tourism practices, government initiatives over eco-friendly travels, an increasing level of biodiversity featured in Indonesia, and most especially nature destinations. Critical destinations that typify eco tour trips to Indonesia are Bali and various iconic destinations: Raja Ampat, Komodo Island National Park, Bromo-Tengger Semeru, and Lake Toba natural wonders that host different or peculiar ecosystems where efforts relating to their conservations can still be undertaken using tourism events.
The "Wonderful Indonesia Ecotourism Initiative," launched by the Indonesian government in 2023, has improved the conditions of eco-tourist travels and attracted those with sensitivity to nature. This effort is for improving sustainable infrastructure and promoting less recognized eco-destinations, plus the seeking of local participation for a truly immersive and natural experience. Bali, Java, and Sumatra remain on top, as these two have built up their established infrastructures and iconic attractions that echo through the world's ecological tourism.
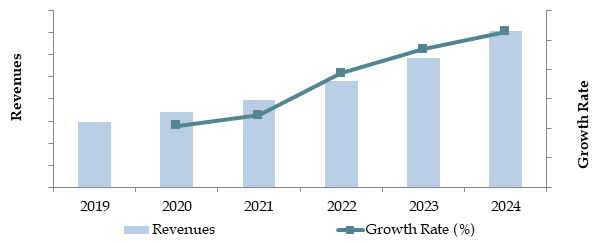
What Factors Are Leading to the Growth of Indonesia Eco-Tourism
Market?
- Rich biodiversity: With a wide array of natural heritage, Indonesia is a home to 17,000 islands, featuring ecosystem types such as rainforests and coral reefs. Countries like Komodo National Park and Raja Ampat are recognized at the global level for being unique in terms of bio-diversity and beckon eco-conscious travelers to their shores. In 2023, more than 30% of international tourists came to Indonesia for eco-tourist experiences.
- Government Initiatives: The government of Indonesia decided to develop a sustainable tourism that would give economic growth and at the same time protect nature. "Green Destinations Indonesia" is one example, including eco-certification, incentives toward local businesses so as to implement environment-friendly practices.
- Rise in Global Eco-Consciousness: Ecotourism in Indonesia is slowly taking shape with the growth in global eco-consciousness about climate change and environmental conservation, leading tourists to seek destinations that will support the concept of sustainability. Ecotourism activities here provide opportunities for tourists to go for ecotourist lodge stays, join wildlife conservation tours, or experience cultural immersion programs, making it attractive for the increasingly large number of visitors.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market?
- Environmental Degradation: Accrued tourist inflow has caused environmental stress like deforestation, coral bleaching, and habitat loss of wildlife in popular eco-destinations. Indeed, a report showed that over-tourism was blamed for declining coral health in as high as 15% of areas like Raja Ampat and Bunaken in the year 2023. Therein lies the daunting task of how to manage sustainable tourism without further environmental degradation.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Poor infrastructure at remote eco-tourism spots makes the place inaccessibly discrete and deters potential travelers from traveling to the area. These are manifested mainly as a shortage of good road connectivity, lack of decent places to stay, and a lack of adequate utilities. This is true, especially in emerging eco-destinations such as Flores and Wakatobi. In 2023, 27% of tourists who had been considering Indonesia for eco-tourism cited inadequacy in infrastructure as one of the deterrents.
- Inability in community participation: With the rise in the adoption of community-based tourism, communities are not always actively involved in the tourism development processes. This generally translates into inadequate ownership, a decrease in the cultural authenticity, and less openness towards the tourism initiatives. In such areas without significant involvement of the local people, the eco-tourism rate was 10% lesser in the growth as compared to the actively engaged regions.
What are the various regulations and initiatives that have governed the market?
- Environmental Protection Laws: The Indonesian government institutes strict regulations in a bid to protect natural ecosystems at eco-tourism hotspots. Laws such as the Environmental Management Act have stipulated rules that ensure operators within tourism adhere to the set rules concerning waste management, pollution control, and habitat conservation. In 2023, the compliance rate of registered eco-tourism operators was 85%.
- Marine Conservation Policy: Regions are pushing ahead, accordingly, with charging mechanisms in place for marine parks, like the guidelines for snorkeling/diving operationally, for places such as Raja Ampat. These policies will be applied with the aim of easing possible environmental damage developed from tourism activities. This paper has identified the ocean park fees as one contributing revenue upward of IDR 150,00,000,00, presented toward conservation in funding, per annum for 2023.
- Eco-Tourism Certification: The government-initiated eco-certification programs, with the hope that this would inspire better, more viable management of tourism. In return, those destinations and operators that achieved certification were granted recognition and incentives. By 2023, 12% of Indonesia's eco-lodges and tour operators had gained such certification under these programs, reflecting emphasis on sustainability.
Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure: In Indonesia, eco-tourism activities are dominated by local operators, considering that they can guarantee more authenticity in experiences, special services, and active participation at the community level. Some of them work with the help of and in cooperation with the local community, thus providing immersion and economic benefits to the region. International tour operators are those who have a good number of shares in this industry. They can cater to international markets and offer a well-structured package deal in various places which may become appealing to foreign tourists looking for convenience and variety.
- By Popular Activities: Marine-based activities are the leading kinds of activities in the country's tourism market, considering Indonesia's lengthy coastline and immense marine biodiversity. The share of other activities, including wildlife treks and rainforest explorations, is also quite substantial because international visitors travel with an interest in spotting unique species, including Sumatra orangutans and Komodo dragons of Komodo National Park. Traditional village visits and handicraft workshops are some popular forms of cultural tourism and attract visitors who like to be engulfed in more community-oriented experiences.
- By Region: Bali is the commanding hub of the eco-tourism market, boosted by its infrastructure, activities on offer, and recognized worldwide as a sustainable holidaying destination. Other recognizable regions include Raja Ampat and Komodo areas that boast pristine natural habitat with conservation efforts attracting high-value international tourists through controlled access. Places like Flores and Sumba are developing as interest shifts to far-flung locations and with government initiatives taken lately.
Competitive Landscape in Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
There's still, however, significant fragmentation as much big movement happening into making contributions or the growth in the segment come under players falling. These include international travel agencies operating locally, online platforms with their packages to offer towards eco-tourism activities, and locally operating tourism agencies. Top players mainly that deal in business eco tours include Green Indonesia Tours, Flores Komodo Eco Tour, I Like Local, Responsible Travel, and Wonderful Indonesia.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|
| Sumatra EcoTravel | 2012 | Bukit Lawang, Sumatra |
| Borneo Eco Tours | 1991 | Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia |
| Bromo Eco Tourism | 2010 | Probolinggo, East Java |
| Adventure Borneo | 2015 | Banjarmasin, South Kalimantan |
| SeaTrek Sailing Adventures | 1985 | Bali, Indonesia |
| Altaï Indonesia | 2010 | Bali, Indonesia |
| LooLa Adventure Resort | 1999 | Bintan Island, Indonesia |
| Gili Eco Trust | 2000 | Gili Trawangan, Lombok |
| Komodo Resort & Diving Club | 2011 | Komodo Island, Indonesia |
| Nikoi Island | 2007 | Bintan Island, Indonesia |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
- Green Indonesia Tours: One of the leading eco-tour operators, specializing in Bali and the surrounding areas, noted a 20% increase in bookings regarding cultural and nature-based tours for 2023. It provides for community engagement in tourism, offering unique experiences related to organic farming and traditional Balinese ceremonies.
- Flores Komodo Eco Tours: Operates in Komodo and Flores and recorded 15% more visitors this year. Their involvement in the local communities and with conservation groups has won them a great reputation among ecotourists.
- I Like Local: Known for its genuine, community-based experiences throughout Indonesia, I Like Local recorded a 30% increase in bookings for rural eco-tourism packages in 2023. Their emphasis on linking tourists with local hosts has gone a long way in building its reputation as a socially responsible platform.
- Government Initiative of Ecotourism Development in Indonesia: A government initiative for ecotourism development, supported by heavy marketing campaigns, began aggressively by 2023 through Wonderful Indonesia in Europe and the US. The best output it saw was in increasing international tourist arrivals-upto 25 percent-and the resultant infrastructural development in less touristy places like Sumba and Kalimantan.
- Responsible Travel: This international player is very strong in Indonesia, with 10% growth in bookings for tailored eco tours reported for this year. It attracts the interest of global ecotourists by offering a carbon footprint reduction and supporting conservation projects.
What Awaits Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market?
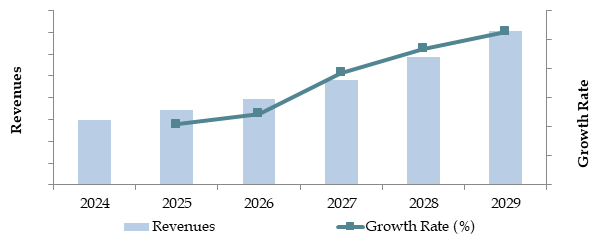
The ecotourism market in Indonesia is likely to record robust growth by 2029 at a significant CAGR throughout the forecast period. This can be attributed to rising international interest in sustainable tourism, promotional initiatives taken by governments to support ecotourism, and increased consciousness regarding protection of the environment among tourists.
- Growing Interest in Secondary Destinations: Popular eco-tourism destination areas such as Bali and Raja Ampat have taken up the challenges brought about by over-tourism; therefore, there should be accordingly more intense marketing activity for lesser-known destinations such as Flores, Sumba, and Kalimantan. Communities within these areas, especially, will see a boost in infrastructural developments to make access to these traditional tourist spots easier both domestically and internationally.
- Expansion of Sustainable Accommodation Options: The expansion of sustainable accommodation options will witness increased demand from tourists for eco-lodges and green-certified accommodations in a bid to have low-impact travel. New developments will be energy-efficient, waste-managed, and locally sourced, in line with global trends on sustainability.
- Integration of Smart Technologies: Adoption of digital platforms, AI, and IoT in managing eco-tourism is bound to further improve visitor experiences. These technologies will enable visitor tracking, real-time resource management, and personalized itinerary planning to make tourism sustainable with increased visitor satisfaction.
- Community-Based Tourism Growth: Community engagement will remain one of the strong pillars in Indonesia's eco-tourism strategy. Such programs that include local populations in the planning, management, and delivery of tourism experiences will be scaled up. This approach not only preserves cultural heritage but also ensures equitable economic benefits for the local communities.
Future Outlook and Projections for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029
Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
- Local Tour Operators
- International Tour Agencies
- Online Travel Platforms
- Community-Based Tourism Programs
- Sustainable Accommodation Providers
- Government-Led Initiatives
- By Popular Activities:
- Snorkeling and Diving
- Wildlife Safaris and Trekking
- Cultural and Heritage Tours
- Marine Conservation Programs
- Rural Tourism and Homestays
- Adventure Sports (e.g., rafting, hiking)
- By Key Destinations:
- Bali
- Raja Ampat
- Komodo National Park
- Bromo Tengger Semeru National Park
- Lake Toba
- Flores and Sumba
- By Transportation Modes:
- Air Travel
- Boat and Liveaboards
- Private Vehicles
- Public Transport
- Sustainable Transport (e.g., bicycles, electric vehicles)
- By Target Demographics:
- Millennials (18-34)
- Families (35-54)
- Seniors (55+)
- International Travelers
- Domestic Travelers
- By Region:
- Sumatra
- Java
- Bali
- Nusa Tenggara
- Sulawesi
- Papua
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- Sumatra EcoTravel
- Borneo Eco Tours
- Bromo Eco Tourism
- Adventure Borneo
- SeaTrek Sailing Adventures
- Altaï Indonesia
- LooLa Adventure Resort
- Gili Eco Trust
- Komodo Resort & Diving Club
- Nikoi Island
Key Target Audience:
- Eco-Tourism Operators
- Government Tourism Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Tourism and Creative Economy)
- Environmental and Conservation Organizations
- Online Travel Marketplaces
- Local Communities and Entrepreneurs
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018-2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process – Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
4.4. Decision-Making Process for Travelers
4.5. Role of Community Engagement in Eco-Tourism Value Chain
5. Market Structure
5.1. Tourist Arrivals in Indonesia, 2018-2024
5.2. Domestic vs. International Tourist Share, 2018-2024
5.3. Eco-Tourism Contribution to Indonesia’s Tourism GDP, 2024
5.4. Number of Eco-Tour Operators by Region
6. Market Attractiveness for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Tourist Volume, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Basis
9.1. By Key Destinations (Bali, Raja Ampat, Komodo, and others), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Pricing Brackets, 2023-2024P
9.3. By Region (Sumatra, Java, Bali and others), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Popular Activities (Diving, Trekking, Cultural Tours, and others), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Transport Modes (Air, Boat, Sustainable Transport, and others), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Traveler Demographics (Domestic, International), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
12. Indonesia Eco-Tourism Financing Landscape
12.1. Tourism Development Grants and Investments, 2018-2029
12.2. Role of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
12.3. Financing Mechanisms for Sustainable Infrastructure Development
12.4. Community Funding and Support Programs
13. Opportunity Matrix for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market – Presented with the Help of Radar Chart
14. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
15. Competitor Analysis for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market
15.1. Market Share of Key Players in Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Operators Basis Revenues, 2023-2024P
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Basis Operational and Financial Parameters
15.3. Strength and Weakness
15.4. Operating Model Analysis Framework
15.5. Operating Model Analysis Framework
15.6. Gartner Magic Quadrant for Market Positioning
15.7. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. Future Market Size for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Basis
16.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
16.2. Tourist Volume, 2025-2029
17. Market Breakdown for Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market Basis
17.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Market), 2025-2029
17.2. By Key Destinations, 2025-2029
17.3. By Pricing, 2025-2029
17.4. By Region, 2025-2029
17.5. By Popular Activities, 2025-2029
17.6. By Transport Modes, 2025-2029
17.7. By Traveler Demographics, 2025-2029
17.8. By Community Engagement Programs, 2025-2029
18. Recommendation
19. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 players in the market based on their tourism volume, sustainability practices, and regional influence.
Sourcing is conducted through industry reports, government publications, academic articles, and multiple secondary and proprietary databases to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Engage in exhaustive desk research by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This includes analyzing market drivers, revenue streams, tourist demographics, and regional segmentation.
Examine company-specific data such as annual reports, sustainability initiatives, press releases, and operational practices to gain insights into key players and market dynamics.
Additional sources include tourism statistics, environmental agency reports, and whitepapers to construct a foundational understanding of the market.
Step 3: Primary Research
Conduct structured interviews with key stakeholders, including eco-tourism operators, conservation organizations, government officials, and local community leaders.
The interview process serves to validate market hypotheses, confirm statistical data, and extract operational insights on eco-tourism challenges, community involvement, and growth strategies.
Bottom-to-top analysis is used to evaluate tourist volumes and revenue contributions of individual operators, aggregating these figures to determine overall market performance.
Disguised interviews are conducted with companies and operators under the guise of potential customers to validate operational and financial data against secondary sources.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Perform top-to-bottom and bottom-to-top analyses alongside market size modeling to ensure consistency and reliability in data findings.
Cross-validation with multiple sources and methodologies ensures accuracy and aligns market estimates with industry trends.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market?
The Indonesia eco-tourism market is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated value of IDR 90 Trillion by 2029. This growth is fueled by the rising global awareness of sustainable travel, Indonesia’s rich biodiversity, and government initiatives promoting eco-friendly tourism. Emerging destinations like Flores and Sumba offer immense potential for development and diversification.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market?
Key players in the Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market include Green Indonesia Tours, Flores Komodo Eco Tours, I Like Local, Wonderful Indonesia (a government initiative), and Responsible Travel. These players are recognized for their focus on sustainability, community engagement, and innovative travel experiences.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market?
Primary growth drivers include Indonesia’s unparalleled biodiversity and natural attractions, strong government support through eco-tourism campaigns, and increased global demand for sustainable travel experiences. The rise of digital platforms has also made eco-tourism destinations more accessible to a wider audience.
4. What are the Challenges in the Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market?
Challenges include environmental degradation from over-tourism, limited infrastructure in remote destinations, and seasonal fluctuations in demand. Additionally, balancing tourism growth with conservation efforts and ensuring equitable economic benefits for local communities remain significant hurdles.

Want to Assess the Impact of US-Imposed Trade Tariff on
Indonesia Eco-Tourism Market